ADVERTISEMENT
Sources of Selenium
To ensure adequate selenium intake, consider incorporating the following selenium-rich foods into your diet:
- Brazil nuts: One of the richest sources of selenium. Just one or two Brazil nuts a day can meet your daily requirement.
- Seafood: Fish such as tuna, halibut, and sardines are excellent sources of selenium.
- Meat: Beef, chicken, liver, and turkey also contain good amounts of this mineral.
- Eggs: Provide selenium along with other essential vitamins and minerals.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oatmeal contain selenium and are a healthier alternative to their refined counterparts.
Supplementing Selenium
While diet is the best way to increase selenium intake, supplements are also available. However, it’s important to use caution with selenium supplements, as too much can be harmful. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for adults is 55 micrograms per day, but this can vary based on age, gender, and health conditions. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Incorporating Selenium in Your Skincare Routine
Besides dietary intake, some topical skincare products contain selenium. These can help provide localized antioxidant benefits directly to the skin. Look for serums and creams that list selenium as an ingredient, especially those designed for anti-aging or skin-brightening.
Conclusion
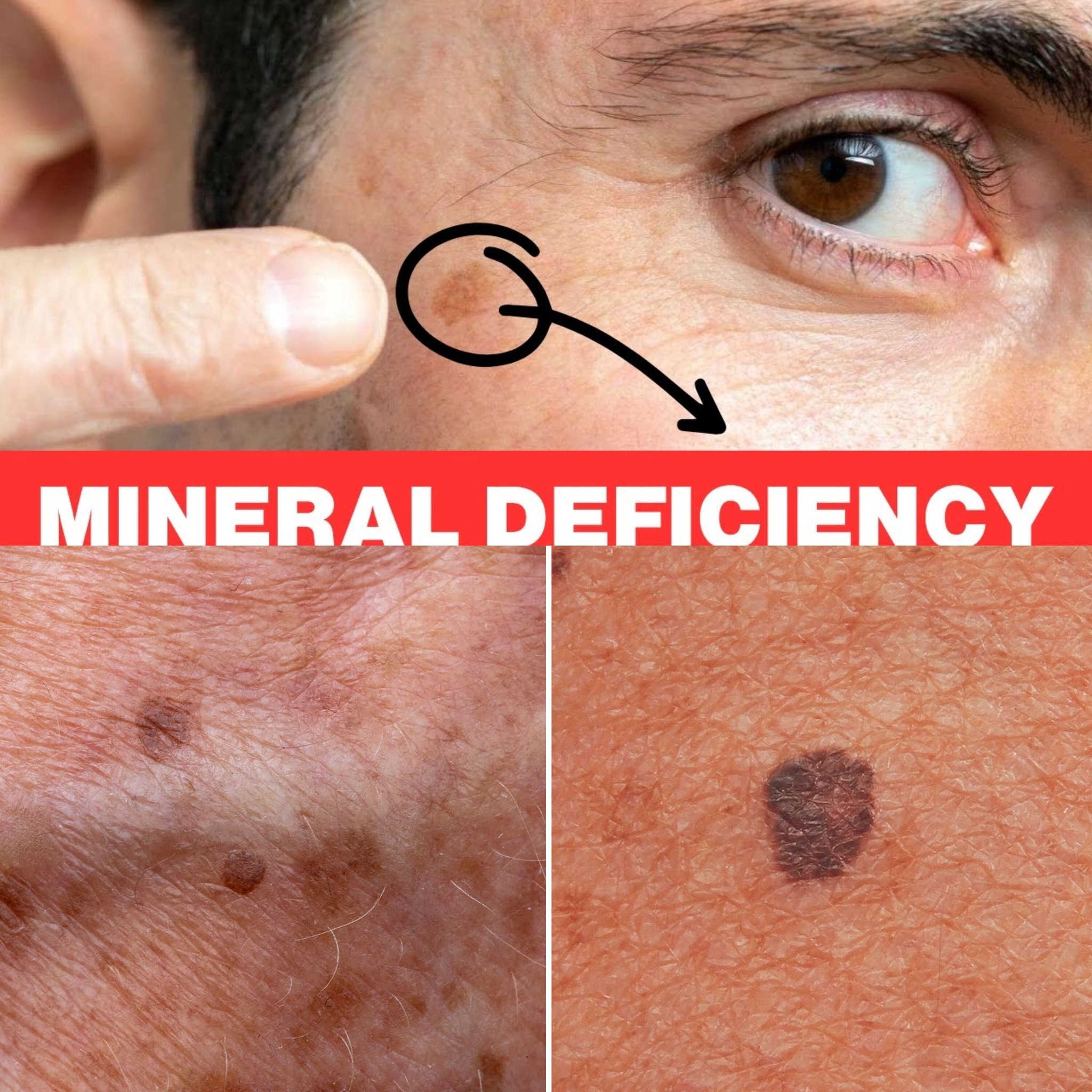
If you’re concerned about age spots and overall skin health, evaluating your selenium intake might provide benefits. By ensuring you receive enough of this vital mineral through diet or supplements, you can help protect your skin from premature aging and improve its overall appearance. Remember, a balanced diet combined with proper skincare practices offers the best defense against age spots and other signs of aging.
ADVERTISEMENT